- What are uterine fibroids
- Uterus fibroids, fibromyoma, and fibroma - what is the difference?
- Causes of uterine fibroids
- Uterine fibroids classification
- When are the uterine fibroids evident?
- How to prevent the uterine fibroids
Symptoms of uterine fibroids: answer these questions to make sure you have/n't uterine fibroids
- Has your menstrual bleeding increased?
- The last 3 periods were more prolonged?
- Are there any clots in the secretions?
- Does the pain during periods become stronger or appear?
- Do you have any heaviness in the lower abdomen and the lower back?
- Any difficulty urinating or more frequent urges?
- Have any of your relatives been diagnosed with uterine myoma?
If most of your answers are yes, you should visit a gynecologist as soon as possible!
What are uterine fibroids?
Uterine fibroids is a disease that occurs in 20% of women aged 30 to 50 years. Fibroids are benign new formations (tumors) in the tissues of the uterus or cervix. The causes of tumor development are not thoroughly studied. It is known that fibroids occur after the uterus damages such as abortions, surgical interventions, curettage. One cell of the muscle or connective tissue begins to divide actively and creates tumor cells assembling into nodes. The development of fibroids depends on the level of reproductive hormones, in particular estrogen. That's why such tumors rarely occur before puberty and after the menopause.Fibroid nodes is not a sufficient reason for the complete uterus removal. In case a doctors offer you such a surgery, it is better to consult with several specialists.
Uterus fibroids, fibromyoma, and fibroma - what is the difference?
Benign formations in the uterus vary according to its origin.
Uterine fibroids are formations (growths) of muscle tissue, fibromas are formed by dividing cells of the connective tissue of the uterus, and fibromyoma consists of connective and muscle tissue.
Although these tumors differ in structure, they are provoked by the same factors. The development of uterus fibroids, fibromyomas and fibromas occur with similar symptoms, is diagnosed and treated in the same way.
An only histological test can identify the structure of the uterus growth.
Causes of uterine fibroids
The reasons for the fibroids development in the female body are not fully understood; the experts say that the tumor (growth) is formed from a cell that has been damaged:
- as a result of the inflammatory process;

- during a surgery;
- by irregular periods;
- due to genetic predisposition.
Further tumor development is controlled by reproductive hormones.
Still, a "damaged" cell is not the only cause of uterine fibroids. A range of additional factors provokes the disease.
Knowing and managing them significantly reduce the risk of the tumor.
The following factors trigger the disease:
- age
Most often, fibroids occur in women of 30-50 y.o. Women of this age have changes in endocrine profile while the fibroids are high sensitive to these changes.
- hormone imbalance
Uterine tissues forming the fibroids are sensitive to female sex hormones. Thus, estrogen and progesterone can influence the size of the tumor. The blood test doesn't represent the change in the level of these hormones in the uterus making the detection of the disease much complicated.
- obesity
Excess body weight affects the level of female sex hormones and increases the risk of uterine fibroids and other conditions.
- you experience constant stress;
- you suffer from excess weight;
- there were cases of the diseases in the family;
- you have an irregular sex life;
- you had an abortion.
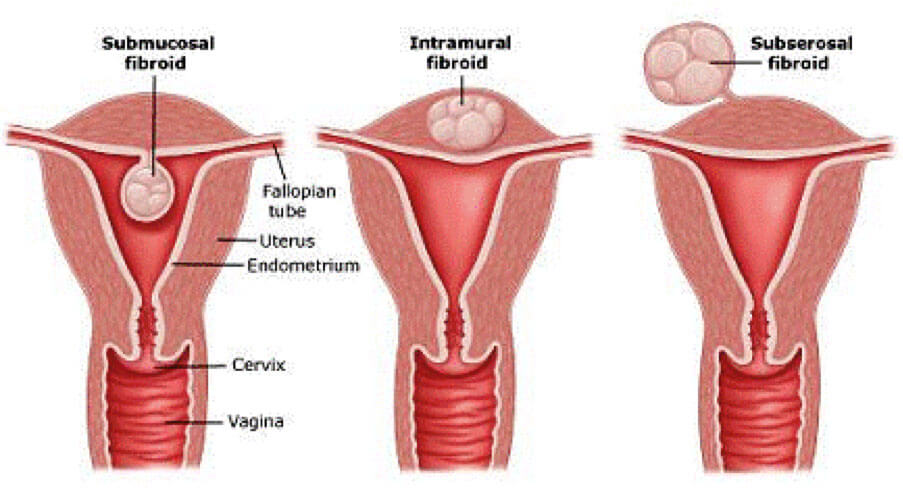
The uterine fibroids classification
The fibroids are classified according to the clinical signs and location in the uterus.
| Type | Localisation | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
Submucous fibroids | A tumor is deeply in the uterus body (under the mucous membranes) and grows towards the endometrium. |
|
Subserosal fibroids | It grows outside the uterus. When it is large enough, expands into the pelvic area. |
|
Intramural fibroids | The nodes appear in the muscles of the uterus. | A tumor of size up to 3 cm has no symptoms. Then the following symptoms are possible:
|
When are the uterine fibroids evident?
Signs of fibroid are not a 100% evidence of the development of this particular pathology. The same symptoms can occur with other gynecological diseases, such as endometriosis, ovarian or uterine cancer, etc.
Small-sized fibroids can show no symptoms. In these cases, a tumor can be detected only during a planned visit to a gynecologist.
How to prevent the uterine fibroids
It is impossible to avoid the uterine fibroids completely. You can only reduce the risk of the development, following a healthy lifestyle, eating correctly and regularly doing sports.
To prevent the disease, you also should:exclude the possibility of abortion;
- have regular gynecological examinations;
- avoid stress;
- avoid overcooling;
- еreat inflammations timely;
- control weight;
- monitor the endocrine profile and regularity of sexual activity.